Kyle Nakatsuji, the author of this article, was a Principal at American Family Ventures, the venture capital arm of American Family Insurance. There he focused on identifying and supporting early-stage companies affecting the future of the insurance industry. American Family Ventures invests across a variety of sectors, including IoT, fintech, SaaS, and data and analytics. Read the original article.
Selling insurance is complicated. Not impenetrable, but complicated. The sales process is sort of like a tangled piece of string— it’s easy to see the beginning and end, but hard to figure out what’s happening in the middle.
When you start untangling, you’ll find prospect lists, telemarketing, direct mail, traditional marketing, and web-based lead generators uncovering and enticing potential customers. You’ll also find captive agents, independent agents or brokers, wholesalers, direct telephone sales, the Internet, affiliates, carriers, and carrier-like entities selling various products.
Some of these strategies work in coordination or create feedback loops — a customer sees a TV ad, which prompts them to submit a form online, which adds them to a direct mail list, that points them to an online aggregator. That puts them in touch with an independent agent selling insurance on behalf of a managing general agency… As you can see, the number of distribution permutations is considerable. This also applies to insurance distribution.
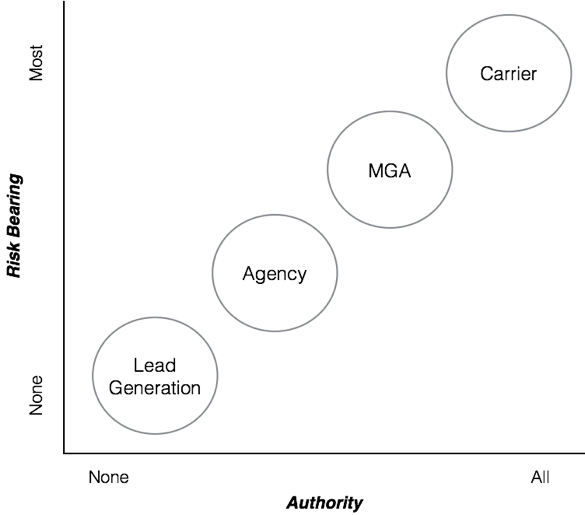
However, at American Family Ventures, we appreciate simplicity. We classify insurance distribution start-ups using four groupings: lead generation, agency/brokerage, managing general agency (MGA), and carrier.
As pictured above, the primary distinctions between participants in each group arise from the amount of insurance risk they bear and their control over certain aspects of the insurance transaction (for example, the authority to bind and underwrite insurance policies).
However, many other trade-offs await insurance start-ups navigating among these four groups. If you consider the evolution of digital customer acquisition, including new channels like mobile-first agencies and incidental channels, choosing a niche becomes even more complicated.
In this post, I’ll discuss some of the key attributes of each group, touching on topics relevant for start-ups new to the insurance ecosystem. Please note, in the interest of time and readability, this post is an overview. In addition, any thoughts on regulatory issues are focused on the U.S. and are not legal advice.
LEAD GENERATION
Lead generation refers to the marketing process of building and capturing interest in a product in order to create a sales pipeline. In the insurance context, because of the high-touch sales process, this historically meant passing interested customers to agents or call centre employees. Today, lead generation operators sell to a variety of third parties, including online agencies and digital sales platforms.
Let’s consider a few key attributes of lead generation providers.
- Revenue model — there are a variety of lead-selling methods, but the most common is pay per lead, where the downstream lead buyer (carrier or channel partner) pays a fixed price for each lead received. When pricing leads, quality plays a big role. Things like customer profile, lead content or data, exclusivity, delivery, and volume all affect lead quality, which frequently drives the buyer’s price sensitivity. As a lead generation provider, you’ll generally make less per customer than others in the insurance distribution chain, but you’ll also assume less responsibility and risk.
- Product breadth — with the Internet and enough money, you can generate leads for just about anything. Ask people who buy keywords for class action lawsuits. However, start-ups should consider which insurance products generate leads at acceptable volumes and margins before committing to the lead generation model. Some products are highly competitive, like auto insurance, and others might be too obscure for the lead model to scale, like alien abduction insurance (which, unbelievably, is a real thing). Start-ups should also consider whether they possess information about customers or have built a trusted relationship with them — the former is often better suited to lead generation and the latter can facilitate an easier transition to agency/brokerage.
- Required capabilities (partnerships) — lead generation providers need companies to buy their data or leads. Their customers are usually the other insurance distribution groups in this post. Sometimes they sell information to larger data aggregators, like Axciom, that consolidate lead data for larger buyers. Generators need to show lead quality, volume, and uniqueness in order to secure relationships with lead purchasers, but beyond that they don’t typically require any special partnerships or capabilities.
- Regulation — while I won’t go into detail here, lead generation operators are subject to a variety of consumer protection laws.
AGENCIES AND BROKERAGES
Entities in the agency/brokerage group (also called producers) come in a variety of forms, including independent agents, brokers, captive agents, and wholesale brokers. Of note, most of these forms exist online and offline.
Independent agents represent a number of insurance carriers and can sell a variety of products. Brokerages are very similar to independent agents in the insurance distribution value chain, having their ability to sell a variety of products, but with a legal distinction — they represent the buyer’s interests, whereas agents represent the carriers they work for. Captive agents, as the name suggests, sell products for only one insurer. While this might seem limiting, captive agents can have increased knowledge of products and the minutiae of policies. Finally, some brokers provide services to other agents/brokers that sell directly to customers. These wholesale brokers place business brought to them by retail agents with carriers, often specialising in unique or difficult placements.
An important difference between the lead generation group and the agency/brokerage group in insurance distribution is the ability to sell and bind policies. Unlike the former, the latter sells insurance directly to the consumer, and in some cases issues binders — temporary coverage that provides protection as the actual policy is finalised and issued.
Some attributes of agencies and brokerages.
- Revenue model — agencies and brokerages generally make money through commissions paid for both new business and on a recurring basis for renewals. The amount you earn in commissions depends on the volume and variety of insurance products you sell. Commission rates for this insurance distribution model vary by product, typically based on the difficulty of making a sale and the value (profitability) of the risk to the insurance carrier. Start-ups should expect to start on the lower end of many commission scales before they can provide evidence of volume and risk quality. Agents and brokers can also be fee-only (paid for service directly and receive no commission), but that’s rare.
- Product breadth — agencies and brokerages sell a variety of products. As a general rule, the more complex the product, the more likely the intermediary will include a person (rather than only software). Start-ups should also consider trade-offs between volume and specialisation. For example, personal auto insurance is a large product line, but carriers looking to appoint agents (more detail below) in this category usually have numerous options, including brick and mortar and online or mobile entities. Contrast this with a smaller line like cyber insurance, where carriers may find fewer, specialist insurance distributors who understand unique customer needs and coverages.
- Required capabilities (partnerships) — agencies and brokerages are appointed by carriers. This process is often challenging, particularly for start-ups, who are non-traditional applicants. Expect the appointment process to take a while if the carrier isn’t familiar with your acquisition strategy or business model. Start-ups trying to accelerate the appointment process can start in smaller product markets (e.g. non-standard auto) or seek appointment as a sub-producer. Sub-producers leverage the existing appointments of an independent agency or wholesaler in exchange for sharing commissions. You could also apply for membership in an agency network or cluster — a group of agents/brokers forming a joint venture or association to create collective volume and buying power in insurance distribution.
- Regulation — agencies and carriers need a license to sell insurance. Each state in the U.S. has its own licensing requirements, but most involve some coursework, an exam, and an application. As we’ve recently seen with Zenefits, most states have a minimum number of study hours required. There are typically separate licenses for property, casualty, life, and health insurance. Once licensed, many states have a streamlined non-resident licensing process, allowing agencies to scale more quickly.
MANAGING GENERAL AGENCIES (MGAs)
A managing general agent (MGA) is a special type of insurance agent/broker in the insurance distribution chain. However, unlike traditional agents/brokers, MGAs have underwriting authority. This means that MGAs are (to an extent) allowed to select which parties or risks they will insure. They also can perform other functions ordinarily handled by carriers, like appointing producers or sub-producers and settling claims.
Start-ups often consider setting up an MGA when they possess data or analytical expertise that gives them an underwriting advantage. The MGA structure allows the start-up more control over the underwriting process, participation in the upside of selecting good risks, and influence over the entire insurance experience, e.g. service and claims.
We’ve recently witnessed MGAs used for two diverging use cases. The first type of MGA exists for a traditional use case — specialty coverages. They are used by carriers who want to insure a specific risk or entity, but don’t own the requisite underwriting expertise. For example, if an insurer saw an opportunity in coverage for assisted living facilities, but hadn’t written those policies before, they could partner with an MGA who specialises in that category and deeply understands its exposures and risks. These specialist MGAs often partner closely with the carrier to establish underwriting guidelines and roles in the customer experience. Risk and responsibilities for claims, service, etc. are shared among the two parties.
The second type of MGA is a quasi-carrier, set up through a fronting program. In this scenario, an insurance carrier (the fronting partner) offers the MGA access to their regulatory licenses and capital reserves to meet the statutory requirements for selling insurance. In exchange, the fronting partner will often take a fee (percentage of premium) and very little (or no) share of the insurance risk. This way, the MGA often has full responsibility for product design and pricing, and looks and feels like a carrier in the insurance distribution chain. They underwrite, quote, bind, and service policies up to a specific amount of written authority. These MGAs are often set up when a start-up wants to control as much of the insurance experience as possible, but doesn’t have the time or capital to establish themselves as an admitted carrier.
Some important characteristics.
- Revenue model – MGAs often get paid commissions, like standard agencies/brokerages, but also participate in the upside or downside of underwriting profit or loss. Participation can come in the form of direct risk sharing (obligation to pay claims) or profit sharing. This risk sharing functions as skin in the game, preventing an MGA from relaxing underwriting standards to increase commissions, which are a function of premiums, at the expense of profitability, which is a function of risk quality.
- Product breadth – MGAs of either type often provide specialised insurance products, at least at first. The specialisation they offer is the reason why customers (and fronting partners) agree to work with them instead of a traditional provider. That said, you might also find an MGA offering standard products, but taking the MGA form, because it has unique customers or a channel for insurance distribution or customers and wants to share in the resulting profits.
- Required capabilities (partnerships) – setting up an MGA generally requires more time and effort than setting up an agency/brokerage. This is because the carrier vests important authority in the MGA, and therefore must work collaboratively with it to build trust, set guidelines, determine objectives, and decide on limits to that authority. Start-ups looking to set up an MGA should be ready to provide evidence they can underwrite uniquely and successfully or have a proprietary channel filled with profitable risks. Fronting often requires a different process, and the setup time required varies based on risk participation or obligations of the program partner. Start-ups should also carefully consider the costs and benefits of being an agency vs an MGA — appointment process difficulty vs. profit sharing, long-term goals for risk assumption, etc. vary across the insurance distribution chain.
- Regulation – MGAs, like carriers, are regulated by state law. They are often required to be licensed producers. Start-ups should engage experienced legal counsel before attempting to set up an MGA.
CARRIERS
Insurance carriers build, sell, and service insurance products. To do this, they often vertically integrate a number of business functions, including some we’ve discussed above — product development, underwriting, sales, marketing, claims, finance and investment, etc.
Carriers come in a variety of forms. For example, they can be admitted or non-admitted. Admitted carriers are licensed in each state of operation, non-admitted carriers are not. Often, non-admitted carriers exist to insure complex risks that conventional insurance marketplaces avoid. Carriers can also be captives — essentially a form of self-insurance where the insurer is wholly owned by the insured. Explaining captives could fill a separate post, but if you’re interested in the model, you can start your research here.
Attributes to consider.
- Revenue model – insurance carrier economics can be complicated, but the basic concepts are straightforward. Insurers collect premium payments from the insured, which they generally expect to cover the costs of any claims (referred to as losses). In doing so, they profit in two ways. The first is pricing coverage so the total premiums received are greater than the amount of claims paid, though there are regulations and/or market pressures that dictate profitability. The second is investing premiums. Because insurance carriers collect premiums before they pay claims, they often have a large pool of capital available, called the float, which they invest for their own benefit. Warren Buffet’s annual letters to Berkshire shareholders are a great source of knowledge for anyone looking to understand insurance economics. Albert Wenger of USV also recently posted an interesting series that breaks down insurance fundamentals.
- Product breadth – carriers have few limitations on which products they can offer. However, the products you sell impact regulatory requirements, required infrastructure, and profitability.
- Required capabilities (partnerships) – carriers can market and sell their products using any or all of the intermediaries for insurance distribution described in this post. While carriers are often the primary risk-bearing entity — they absorb the profits and losses from underwriting — in many cases they partner with reinsurers to hedge against unexpected losses or underperformance. There is a variety of reinsurance structures, but two common ones are excess of loss (reinsurer takes over all payment obligations after the carrier pays a certain amount of losses) and quota share (reinsurer pays a fixed percentage of every loss).
- Regulation – I’ll touch on a few concepts, but carrier regulation is another complex topic I won’t cover comprehensively in this post. Carriers must secure the appropriate licenses to operate in each country or state (even non-admitted carriers, who still have some regulatory obligations). They also have to ensure any capital requirements issued by regulators are met. This means keeping enough money on the balance sheet (reserves or surplus) in order to ensure solvency and liquidity, i.e. maintaining an ability to pay claims. Carriers also generally have to prove their pricing is adequate, not excessive, and not unfairly discriminatory by filing rates (their pricing models) with state commissioners. Rate filings can be file and use (pre-approval not required to sell policies) or prior approval (rates must be approved before you can sell policies).
Conclusion
In this overview, I did not address a number of other interesting topics, including trade-offs between group choices. For example, you should also consider things like exit or liquidity expectations, barriers to entry, and creating unfair advantages before starting an insurance business. However, hopefully this brief summary sparks questions and new considerations for start-ups entering the insurance distribution value chain.
If you are looking for insurance software for your insurance business, whether a carrier, agency, or MGA, reach out to us!